Please use this identifier to cite or link to this item:
https://hdl.handle.net/2445/221618| Title: | Blood vessels: aorta |
| Other Titles: | Vasos sanguinis: aorta |
| Author: | Pérez Clausell, Jeús |
| Keywords: | Artèries Vasos sanguinis Histologia Aorta |
| Issue Date: | 2025 |
| Abstract: | [ENG] Collection of micrographs on the organisation of the arterial wall in the aorta -thoracic and abdominal- in paraffin sections and epoxy, semithin sections. Samples from rats and other species. The three tunicae -intima, media and adventitia- are shown, including the layered pattern of elastic fibres in the tunica media. [CAT] Col·lecció de micrografies de l'organització de la paret de l'aorta (toràcica i abdominal) en talls de parafina i talls semifins de resina epoxy. Mostres de rata i altres espècies. Es mostren les tres túniques (íntima, mitjana i adventícia) amb la laminació característica de les fibres elàstiques en la túnica mitjana. |
| URI: | https://hdl.handle.net/2445/221618 |
| Appears in Collections: | OMADO (Objectes i MAterials DOcents) |
Files in This Item:
| File | Description | Size | Format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P_O_aorta_HEosin_2x_25_LETTERS.jpg | Transversal section of the aorta in a rat, and the adjoining brown fat (bf) masses. A smaller artery (a) and a vein (v) are seen to the right (not identified, perhaps a bronchial artery and the azygos vein). Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 330.72 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_HEosin_2x_25.jpg | Transversal section of the aorta in a rat, and the adjoining brown fat masses. No labelling. | 321.54 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_HEosin_20x_28_LETTERS.jpg | The aorta wall in a rat. The tunica intima is not sharply delineated, but the tunica media (tm) is heavily stained. The tunica adventitia (ta) shows collagen fibres (lightly stained in this slide; see the aorta abdominalis in another micrograph). The tunica adventitia continues with more connective tissue, brown fat (bf) and a vein (v). Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 641.85 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_HEosin_20x_28.jpg | The aorta wall in a rat. No labelling. | 623.4 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_HEosin_50x_31_LETTERS.jpg | The tunica media (tm) in the rat aorta (and in other elastic arteries) is thick, and consists in multiple layers of elastic fibres (white arrows) darkly stained with eosin, and interspersed layers of smooth muscle cells (nuclei stained in blue). In comparison, the tunica adventitia (ta) is thinner and includes collagen fibres and some vessels (v): the vasa vasorum. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 592.17 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_HEosin_50x_31.jpg | Tunica media and tunica adventitia in the rat aorta. No labelling. | 553.08 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_abdominal_HEosin_4x_51_LETTERS.jpg | The aorta abdominalis is organised in three layers: a thin tunica intima (ti), a thick, heavily stained tunica media (tm), and a moderately stained tunica adventitia (ta). A portion of the vena cava inferior, with a much thinner wall is observed at the top. Unknow species (Department collection), paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin. | 885.29 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_abdominal_HEosin_4x_51.jpg | The wall in the aorta abdominalis. No labelling. | 865.78 kB | JPEG | 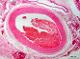 View/Open |
| P_aorta_abdominal_HEosin_16x_54_LETTERS.jpg | Section of an elastic artery (aorta abdominalis). In the thin tunica intima (ti), only the nuclei of endothelial cells can be noticed (arrows). The tunica media (tm) is rich in elastic fibres, forming a multilayered pattern. The elastic fibres just underneath the tunica intima are more conspicuous and form the internal elastic lamina (iel), while those at the border with the tunica adventitia form the external elastic lamina (eel). Those laminae are more conspicuous in muscular arteries. Due to muscle cell contraction during sample fixation, elastic fibres are folded resembling the battlement or crenellations in a castle wall (see “iel”). The tunica adventitia (ta) contains collagen fibres and is more lightly stained. Unknow species (Department collection), paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin. | 764.69 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_abdominal_HEosin_16x_54.jpg | Section of an elastic artery (aorta abdominalis). No labelling. | 745.08 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_abdominal_HEosin_40x_55_LETTERS.jpg | Section of an elastic artery (aorta abdominalis). As in the previous micrograph, the thin tunica intima is only noticeable by the nuclei of the endothelial cells (ti). In the tunica media (tm), crenellated layers of elastic fibres (ef) are seen, standing out the inner elastic lamina (iel) with marked foldings, and the external elastic lamina (eel). Layers of smooth muscle cells are located in between. Collagen fibres (light pink) are present in the tunica adventitia. Unknow species (Department collection), paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin. | 511.63 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_abdominal_HEosin_40x_55.jpg | Section of an elastic artery (aorta abdominalis). No labelling. | 463.25 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_abdominal_infCava_HEosin_6_3x_52_LETTTERS.jpg | Wall of a large vein (vena cava inferior, next to the aorta abdominalis, and the ureters –not shown). The wall is much thinner than the accompanying artery. In contrast to arteries, the muscled tunica media (tm) is thinner than the tunica adventitia (ta). Unknow species (Department collection), paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin. | 745.96 kB | JPEG | 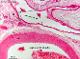 View/Open |
| P_aorta_abdominal_infCava_HEosin_6_3x_52.jpg | Wall of a large vein (vena cava inferior, next to the aorta abdominalis). No labelling. | 714.04 kB | JPEG | 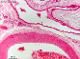 View/Open |
| P_CAVA_inferior_HEosin_40x_57_LETTERS.jpg | Wall of a the vena cava inferior. The tunica intima is formed by flat, thin, endothelial cells, which are not visible except for the nuclei (endothelium, arrows). The tunica media (tm) includes some smooth muscle cells and elastic fibres (crenellated surfece on the right corner). In contrast to arteries, the tunica adventitia is much thicker than the intima and includes collagen fibres (light pink background) and fibroblasts (dark blue). Unknow species (Department collection), paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin. | 435.35 kB | JPEG | 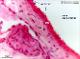 View/Open |
| P_CAVA_inferior_HEosin_40x_57.jpg | Wall of a the vena cava inferior. No labelling. | 408.16 kB | JPEG | 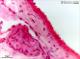 View/Open |
| P_aorta_human_4x_48_50_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Section of a human aorta stained for elastic fibres. A huge number of elastic fibre layers in dark purple (white arrowheads) are densely packed in a wide tunica media (tm). The tunica adventitia (ta), at the top, does not show elastic fibres, and contains some blood vessels: vasa vasorum (vv). Human (Department collection), paraffin section; stain not mentioned, possibly orcein or resorcin. | 1.83 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_human_4x_48_50_collage.jpg | Section of a human aorta stained for elastic fibres. No labelling. | 1.82 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_4x_01_LETTERS.jpg | Semithin section of a rat aorta and the adjoining brown fat. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 484.65 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_4x_01.jpg | Semithin section of a rat aorta and the adjoining brown fat. No labelling. | 463.63 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_semithin_2um_6_3x_11_LETTERS.jpg | Semithin section of a rat aorta lightly stained with toluidine blue. Layers of elastic fibres in the tunica media (tm) are darkly stained in blue. Collagen fibres in the tunica adventitia (ta) are faintly stained. Lipid droplets in the brown fat appear in black because of the OsO4 postfixation. Epoxy section 2 µm thick. | 616.27 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_semithin_2um_6_3x_11.jpg | Semithin section of a rat aorta lightly stained with toluidine blue. No labelling. | 598.99 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_20x_03_LETTERS.jpg | Semithin section of a rat aorta stained with toluidine blue. In the tunica intima (ti), the nucleus of endothelial cells (arrow) is the only noticeable element. In the tunica media (tm), several concentric layers of elastic fibres (in dark blue) can be observed. In the tunica adventitia (ta), loosely arranged collagen fibres are present. Loose connective tissue joins the aorta wall and a mass of brown fat, including a mast cell (in purple). Granules in mast cells are metachromatic: the molecules of this dye bind repetitive polysaccharides, and the highly-organised dye molecules create a purple interference with light, although the dye is blue. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick. | 764.83 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_20x_03.jpg | Semithin section of a rat aorta stained with toluidine blue. No labelling. | 740.94 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_semithin_2um_16x_13_LETTERSb.jpg | Semithin section of a rat aorta lightly stained with toluidine blue. In the tunica media (tm), several concentric layers of elastic fibres (in dark blue) can be observed (arrows). In the tunica adventitia (ta), loosely arranged collagen fibres are palely stained. In the adjoining fat, white adipocytes (wa) with a large, single lipid droplet (in dark grey) are seen close to brown adipocytes (ba) containing multiple, small droplets. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick. | 605.98 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_semithin_2um_100x_18_LETTERS.jpg | Rat aorta at high magnification. The layers of elastic fibres (white arrows) in the tunica media are darkly stained. In between , the muscle cell layers are lighter with dark nuclei (m). A small portion of the tunica adventitia, with collagen fibres, is shown in the upper right corner. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick. toluidine blue stain. | 694.11 kB | JPEG | 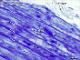 View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_semithin_2um_100x_18.jpg | Rat aorta at high magnification. No labelling. | 645.57 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
This item is licensed under a
Creative Commons License



