Please use this identifier to cite or link to this item:
https://hdl.handle.net/2445/222162| Title: | Blood vessels: muscular arteries, arterioles and capillaries |
| Other Titles: | Vasos sanguinis: artèries musculars, arterioles i capil·lars |
| Author: | Pérez Clausell, Jeús Universitat de Barcelona. Departament de Biologia Cel·lular, Fisiologia i Immunologia |
| Keywords: | Artèries Histologia Microscòpia Vasos sanguinis Artèries |
| Issue Date: | 2025 |
| Citation: | Cite as: Pérez-Clausell J (2025). Blood vessels: muscular arteries, arterioles and capillaries. Universitat de Barcelona, Dipòsit Digital [consulted on 2025/07/11] https://hdl.handle.net/2445/222162 |
| Abstract: | [ENG] Collection of micrographs on the organisation of muscular arteries, arterioles, and capillaries in paraffin sections and epoxy, semi-thin sections. Samples from rats and other species. In muscular arteries, smooth muscle cells in the tunica media are shown. Collagen fibres can be seen in the tunica adventitia. This collection complements the micrographs published by Dr Elena Sagristà i Mateo https://diposit.ub.edu/dspace/browse?type=author&value=Sagrist%C3%A0+i+Mateo%2C+Elena [CAT] Col·lecció de micrografies de l'organització de les artèries musculars, arterioles i capil·lars en talls de parafina i talls semifins de resina epoxi. Mostres de rata i altres espècies. En les artèries musculars s’observa la capa gruixuda de musculatura llisa de la túnica mitjana i les fibres de col·lagen de la túnica adventícia. Aquesta col·lecció complementa les micrografies publicades per la Dra. Elena Sagristà i Mateo https://diposit.ub.edu/dspace/browse?type=author&value=Sagrist%C3%A0+i+Mateo%2C+Elena |
| URI: | https://hdl.handle.net/2445/222162 |
| Appears in Collections: | OMADO (Objectes i MAterials DOcents) |
Files in This Item:
| File | Description | Size | Format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P_O_tongue_HEosin_20x_35_LETTERS.jpg | Muscular artery in deep regions of the rat tongue. In the tunica intima (ti) only the nuclei of endothelial cells are visible, protruding from the vessel surface. The tunica media (tm) is thicker than the tunica adventitia (ta). This vessel lies next to nerve branches (n) and runs between bundles of striated muscle (st). Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 921.04 kB | JPEG | 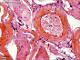 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_HEosin_20x_35.jpg | No labelling. | 900.12 kB | JPEG | 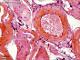 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_HEosin_50x_48_LETTERS.jpg | Detail of a muscular artery wall in the rat tongue. The tunica intima (ti) consists of a simple squamous epithelium ─the endothelium─ with flattened cell nuclei (arrows) stained dark blue with hæmatoxylin. The tunica media (tm) contains smooth muscle cells with oval or elongated nuclei (nu, lighter blue). The tunica adventitia (ta) includes thick collagen fibres (arrowheads) stained pink with eosin, along with connective tissue cells (stained dark blue with hæmatoxylin), for example, fibroblasts. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 623.15 kB | JPEG | 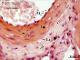 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_HEosin_50x_48.jpg | No labelling. | 587.24 kB | JPEG | 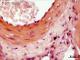 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_vGieson_20x_90_LETTERS.jpg | Muscular arteries deep within the rat tongue. In van Gieson trichrome stain, collagen fibres (col) –and connective tissue, in general– appear dark pink, stained with acid fuchsin. Collagen fibres can be seen between striated muscle bundles (st, light brown) and around two arteries. In the larger artery (bottom), endothelial cell nuclei are seen in the tunica intima (ti). A thick tunica media (tm) of smooth muscle cells (in brown) is surrounded by the tunica adventitia (ta) rich in collagen fibres. In the small artery (top) the same tunicae can be recognised. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. e, erythrocytes. | 850.58 kB | JPEG | 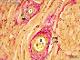 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_vGieson_20x_90.jpg | No labelling. | 819.01 kB | JPEG | 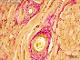 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_vGieson_50x_94_LETTERS.jpg | Muscular artery in the rat tongue. The lumen shows some erythrocytes (e) stained yellow with picric acid. Endothelial cell nuclei in the tunica intima (ti) stand out from the inner surface. In the tunica media (tm), the nuclei of smooth muscle cells (nu) are observed. In the tunica adventitia (ta), thick collagen fibres (arrowheads) are present. The artery is surrounded by striated skeletal muscle fibres (st). Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 778.31 kB | JPEG | 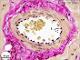 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_vGieson_50x_94.jpg | No labelling. | 748.5 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_vGieson_50x_72_LETTERS.jpg | Muscular artery and surrounding tissue deep within the rat tongue. The lumen includes some erythrocytes (e) stained with picric acid. Endothelial cell nuclei in the tunica intima (ti) are darkly stained with Weigert’s hæmatoxylin, and protrude from the inner surface. In the tunica media (tm), smooth muscle cell nuclei (nu) appear dark brown. Thick collagen fibres (arrowheads) are present in the tunica adventitia (ta). To the right, a small, flattened arteriole (a) is observed, presenting a single layer of smooth muscle cells (sm). Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. st, striated muscle. | 752.35 kB | JPEG | 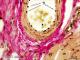 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_vGieson_50x_72_.jpg | No labelling. | 714.54 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b23_b28_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Micrograph of a muscular artery in the rat tongue. A curved segment of the artery is cut, rendering two profiles (a₁, a₂). The tunica media (tm) contains smooth muscle cells and is bordered by a prominent internal elastic lamina (iel, dark blue) and a less distinct external elastic lamina (eel). A thick tunica adventitia (ta) surrounds the artery. Smaller blood vessels (v), venules or capillaries, are seen all over. Osmium tetroxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. n, myelinated nerve; st, striated/skeletal muscle. | 1.13 MB | JPEG | 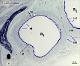 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b23_b28_collage.jpg | No labelling. | 1.08 MB | JPEG | 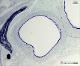 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_20x_b01_LETTERS.jpg | The core of the tongue in a rat. A muscular artery (a₁, a₂), nerve branches with myelinated axons (n), and small vessels (v) are located between bundles of striated/skeletal muscle (st). A turn in the artery was sectioned and two fused profiles (a₁, a₂) can be observed. This muscular artery includes a tunica media (tm) made of densely-packed, smooth muscle cells, bordered by the internal elastic lamina (iel, dark blue) and a less distinct external elastic lamina (eel). Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. ta, tunica adventitia. | 669.09 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_20x_b01.jpg | No labelling. | 620.67 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b02_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Wall of a muscular artery deep within the rat tongue. The round profiles of transversally cut, smooth muscle cells (sm) can be seen in the tunica media (tm). This tunica is bordered by the internal elastic lamina (iel, heavily stained with toluidine blue) and a thin, uneven external elastic lamina with sparse elastic fibres (dashed arrows). The tunica adventitia (ta) merges with the surrounding connective tissue, which includes lightly stained collagen fibres (col, arrowheads). Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. v, small blood vessels. | 688.53 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b02_collage.jpg | No labelling. | 622.74 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_100x_b35_LETTERS.jpg | Muscular artery wall in the core of the rat tongue. Elastic fibres in the internal elastic lamina (iel) are heavily stained with toluidine blue. Isolated elastic fibres (e) are also seen in deeper zones. The tunica media (tm) contains several layers of smooth muscle cells (sm). The tunica adventitia (ta) contains lightly stained collagen fibres (arrowheads). Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. v, small blood vessel in the connective tissue. | 709.59 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_100x_b35.jpg | No labelling. | 656.87 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b18_LETTERS.jpg | Several muscular arteries deep within the rat tongue. A large artery is sectioned longitudinally (a₁) and presents a tunica media (tm) filled with smooth muscle cells, limited by the internal elastic lamina (iel) and, on the opposite side, by the tunica adventitia (ta). A smaller artery (a₂) is cut obliquely, and both tunicae ─media (tm) and adventitia (ta)─ can be seen. Artery profiles a₃ and a₄ could be branches or turns of the former artery. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. st, striated/skeletal muscle fibres. | 756.59 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b18.jpg | No labelling. | 718.73 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b09_LETTERS.jpg | Micrograph of the microvascular system in the rat tongue. Arterioles (a) are smaller than 100 µm in diameter, with an internal elastic lamina (iel) and up to three layers of smooth muscle cells (sm) (Geneser, 1986). Metarterioles (mₐ) or precapillary sphincters are thinner than 30 µm, with no elastic lamina. Capillaries (c) are much thinner. Venules (vn) are larger and with a thin wall. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. n, myelinated nerve; st, striated/skeletal muscle; star, an unidentified vessel, probably a venule (pericytic or muscular). | 899.18 kB | JPEG | 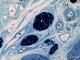 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b09.jpg | No labelling. | 878.1 kB | JPEG | 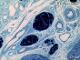 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b10_LETTERS.jpg | Micrograph of arterioles and venules in the rat tongue. Arterioles (a₁, a₂) have an internal elastic lamina (iel) and 1–3 layers of smooth muscle cells (sm). Arteriole a₂ was sectioned longitudinally, and muscle cells show round profiles (sm, arrows). Arterioles run next to postcapillary venules (pc; longitudinal cut; or it could be just a capillary), and collecting venules (vnˬc) 30 µm to 50 µm in diameter with walls lacking muscle cells. Nerves (n) present myelinated axons (n) in which myelin sheaths appear as dark rings due to osmium postfixation (n, white arrowhead), while some axonal branches appear to be unmyelinated (n, black arrowhead). Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. st, striated/skeletal muscle; wa, white adipocyte. | 849.38 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_50x_b10.jpg | No labelling. | 810.94 kB | JPEG | 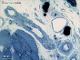 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_100x_b38_LETTERS.jpg | Micrograph of arterioles and venules in the rat tongue. The arteriole features an internal elastic lamina (iel) surrounded by smooth muscle cells (sm) with round or elongated profiles, depending on the plane of sectioning. No external elastic lamina is present, and the muscle cells are surrounded by collagen fibres (col, arrowheads). The metarteriole (ma) has a thinner wall, without internal elastic lamina, and fewer muscle cells. Postcapillary venules (pc) can be up to 30 µm in diameter, with thin walls devoid of muscle cells but containing pericytes. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. c, capillary; n, myelinated nerve. | 763.17 kB | JPEG | 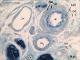 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_100x_b38.jpg | No labelling. | 729.88 kB | JPEG | 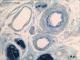 View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_100x_b39_LETTERS.jpg | Micrograph of arterioles and venules in the rat tongue. The arteriole includes an internal elastic lamina (iel) surrounded by smooth muscle cells (sm) and next to it collagen fibres (col, arrowheads) in the connective tissue. A connective tissue cell (cc) filled with secretory granules could be a mast cell (granules appear blue, though typically metachromatic in pink or purple). The venule (pc) could be a postcapillary venule (Ø < 30 µm) or a collecting venule (Ø > 30 µm), both lacking muscle cells in the wall but containing flat pericytes. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. n, myelinated nerves. | 750.39 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_tongue_semithin_2um_100x_b39.jpg | No labelling. | 725.92 kB | JPEG | 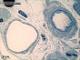 View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_50x_04_LETTERS.jpg | Arteriole (a) in brown fat in a rat. In the endothelium, only the dark, flattened nuclei of endothelial cells (e) can be noticed. A single layer of smooth muscle cells with oval nuclei (sm) is present. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. ba, brown adipocyte; c, capillary; wa, white adipocyte. | 725.73 kB | JPEG | 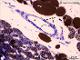 View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_50x_04.jpg | No labelling. | 705.19 kB | JPEG | 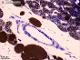 View/Open |
| P_aorta_semithin_2um_40x_34_LETTERS.jpg | Arteriole (A) in brown fat in a rat. In the endothelium, only the dark, flattened nuclei of endothelial cells (en) can be noticed. A layer or two of smooth muscle cells with oval nuclei (sm) can be seen. Between the brown adipocytes (ba), Capillaries (c) contain small, white lumina which are lined by crescent-shaped, dark endothelial cell nuclei. They are interspersed between brown adipocytes. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. ba, brown adipocyte; c, capillary; wa, white adipocyte. | 474.23 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_semithin_2um_40x_34.jpg | No labelling. | 502.63 kB | JPEG | 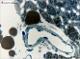 View/Open |
| P_O_oesophagus_HEosin_50x_34_collage_bis_LETTERS.jpg | Capillaries in the connective tissue of the rat oesophagus. Those blood vessels can be as small as 5 µm in diameter. In the lamina propria (pro), three capillaries are seen with an empty lumen (arrowheads) lined by a thin epithelium, where only the flat nuclei of endothelial cells (e) are noticeable. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. epi, stratified epithelium; mus, muscular layer. | 654.87 kB | JPEG | 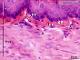 View/Open |
| OP_oesophagus_HEosin_50x_34_collage_bis.jpg | No labelling. | 611.49 kB | JPEG | 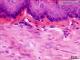 View/Open |
| P_O_stomach_vGieson_50x_54_LETTERS.jpg | Capillaries in the gastric mucosa in a rat. A longitudinally sectioned capillary is seen on the left. The lumen is empty (arrowhead) and the wall is made of endothelial cells, only noticeable by their nuclei (e), and delicate collagen fibres stained pink with acid fuchsin. A transversal capillary profile is seen on the right, with an empty lumen (arrowhead) and a dark brown, crescent-shaped endothelial cell nucleus (e). A larger vessel, probably a postcapillary venule (vn), is seen above. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 535.69 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_stomach_vGieson_50x_54.jpg | No labelling. | 516.88 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_100x_15_LETTERS.jpg | Arteriole and capillaries in brown fat in a rat. In the arteriole (on the right), endothelial cell nuclei are dark and flattened (e). The arteriole wall is reinforced by a single layer of smooth muscle cells with oval nuclei (sm). Numerous capillaries (c) are seen, each with an empty lumen (in white) and crescent-shaped, dark, endothelial cell nuclei (e) in their walls. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 741.9 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_100x_15.jpg | No labelling. | 723.88 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_100x_20_LETTERS.jpg | Capillaries in brown fat in a rat. Capillaries (c) show a white, empty lumen and crescent-shaped, dark, endothelial cell nuclei (e) in their walls. Osmium postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 781.61 kB | JPEG | 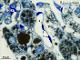 View/Open |
| P_O_aorta_brownFat_semithin_2um_100x_20.jpg | No labelling. | 772.75 kB | JPEG | 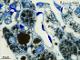 View/Open |
| P_aorta_semithin_2um_100x_39_Capil_LETTERS.jpg | Capillaries in brown fat in a rat. Capillaries (c) are sectioned in various planes and show white, empty lumina and crescent-shaped, dark, endothelial cell nuclei (e) in their walls. Brown adipocytes (ba) enclose small lipid droplets (almost black due to the osmium tetroxide postfixation). Epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. N, adipocyte nucleus. | 472.49 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_aorta_semithin_2um_100x_39_Capil.jpg | No labelling. | 460.06 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
This item is licensed under a
Creative Commons License



