Please use this identifier to cite or link to this item:
https://hdl.handle.net/2445/223556| Title: | Histological organisation of the rat duodenum |
| Other Titles: | Organització histològica del duodè de la rata. |
| Author: | Pérez Clausell, Jeús Universitat de Barcelona. Departament de Biologia Cel·lular, Fisiologia i Immunologia |
| Keywords: | Histologia Duodè Rates (Animals de laboratori) Imatges |
| Issue Date: | 2025 |
| Citation: | Cite as: Pérez-Clausell J (2025) << Title>>. Universitat de Barcelona, Dipòsit digital [consulted on <<date>>] https://hdl.handle.net/2445/?????? |
| Abstract: | [ENG] A collection of micrographs of the duodenum in rats and mice. General views of the intestinal wall and detailed images of each layer are shown: mucosa – comprising the epithelium, lamina propria and muscularis mucosæ –, submucosa, muscularis externa and serosa. Specific structures such as the brush border, goblet cells, crypts, Brunner's glands, and nerve ganglia – both submucosal and myenteric – are also illustrated. Paraffin sections were stained with hæmatoxylin-eosin or van Gieson's trichrome, while epoxy semi-thin sections (2 µm thick) were stained with toluidine blue.
This collection complements the micrographs published by Dr Elena Sagristà i Mateo → https://hdl.handle.net/2445/60214 ← See also: → https://diposit.ub.edu/dspace/browse?type=author&value=Sagrist%C3%A0+i+Mateo%2C+Elena ← [CAT] Col·lecció de micrografies de l'organització del duodè de la rata i ratolí. S'inclouen imatges de la paret intestinal i detalls de cada capa: mucosa (que inclou l'epiteli, làmina propria, muscularis mucosæ), submucosa, muscularis externa i serosa. També es mostren detalls de l'epiteli en raspall, les cèl·lules caliciformes, les criptes, les glàndules de Brunner i els ganglis dels plexes submucós i mientèric. S'han utilitzat talls de parafina tenyits amb hematoxilina-eosina o el tricròmic de van Gieson, i talls semifins de 2 µm tenyits amb blau de toluïdina. Aquesta col·lecció complementa les micrografies publicades per la Dra. Elena Sagristà i Mateo → https://hdl.handle.net/2445/60214 ← See also: → https://diposit.ub.edu/dspace/browse?type=author&value=Sagrist%C3%A0+i+Mateo%2C+Elena ← |
| URI: | https://hdl.handle.net/2445/223556 |
| Appears in Collections: | OMADO (Objectes i MAterials DOcents) |
Files in This Item:
| File | Description | Size | Format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P_intestine_Heosin_ 4x_01_LETTERS.jpg | Wall of the small intestine in mice. Folds of the mucosa form finger-shaped projections termed villi (black arrowheads). These consist of a thin epithelium (ep), stained pink, and loose connective tissue within: the lightly stained lamina propria (lp). The epithelium invaginates into the wall, forming pit-like structures: the crypts. The muscularis mucosæ (mm), the deepest layer of the mucosa, is a thin strip of smooth muscle cells, and is just perceptible at this magnification. Beneath the muscularis mucosæ lies a thin submucosa (sub) and the muscularis externa (me). In the lumen of the intestine, partially digested food is visible, including portions of vegetables with polygonal cell walls (asterisks). Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. v, blood vessels. | 980.66 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_ 4x_01.jpg | Wall of the small intestine in mice. No labelling. | 942.85 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_6_3x_03_04_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Wall of the small intestine in mice in oblique section (collage of micrographs allowing moderate zoom). The mucosa forms outward projections known as villi, which are lined with a simple (mono-layered) columnar epithelium (ep) stained darkly. Although the cytoplasm in most cells stains dark pink, goblet cells (Go) are distributed throughout the epithelium and contain round accumulations of mucous secretory granules that stain bluish-grey (white arrowheads). The epithelium extends into the wall, forming crypts that reach deep portions of the mucosa. The core of the villi and the space between the crypts is occupied by loose connective tissue – the lamina propria (lp) – which is palely stained. The inner or deeper border of the mucosa is marked by a thin muscularis mucosæ (mm), and beneath it lies a denser connective tissue – the submucosa (sub) –, which stains light pink but darker than the lamina propria. Both lamina propria and submucosa are profusely supplied by blood vessels (v). Situated below is the muscularis externa (me), a layer of smooth muscle cells divided into two sublayers, although not distinguishable at this magnification. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 837.34 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_6_3x_03_04_collage.jpg | Wall of the small intestine in mice in oblique section (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 786.13 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_20X_63_66_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Longitudinal section of the duodenum in a rat (collage of micrographs allowing moderate zoom). Three villi are shown lined with a simple epithelium (ep) that also invaginates into the lightly stained lamina propria (lp), forming long crypts. The lamina propria is limited internally by a thin layer of smooth muscle cells – the muscularis mucosæ (mm) – that stains pink. Underneath, the submucosa (sub) is expanded, containing numerous secretory glands (g) – Brunner's glands – with dark purple cell nuclei and pale cytoplasm. Numerous blood vessels (v) are seen here, as in the lamina propria. Deeper, the muscularis externa can be seen divided into two distinct layers: an inner or circular layer (ic) and an outer or longitudinal layer (ol). Since this is a longitudinal section of the duodenum, muscle cell nuclei appear round in the circular layer (transversely sectioned) and elongated in the longitudinal layer. A thin serosa (ser) envelopes the intestine. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. Go, goblet cells. | 1.32 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_20X_63_66_collage.jpg | Longitudinal section of the duodenum in a rat (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 1.25 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_20X_67_69_collageB_LETTERS.jpg | Oblique section of the small intestine in a rat (collage of micrographs allowing moderate zoom). In the labelled villus (centre), the lamina propria (lp) contains numerous vessels (v) and is surrounded by a simple columnar epithelium (ep) consisting of tall cells (white bidirectional arrows) with dark pink cytoplasm and dark purple nuclei, which are aligned in a single row at the basal portion of the cells. Intercalated between these cells, goblet cells (Go) with round, palely-stained accumulations of mucus are observed (white arrowheads). In deeper portions of the mucosa, crypts are cut transversely and appear discontinuous from the surface epithelium, although they are indeed connected. The inner border of the mucosa is defined by the thin muscularis mucosæ (mm) consisting of smooth muscle cells, which stain intensely pink. The submucosa (sub) is thin in this portion of the intestine, but rich in collagenous fibres, and stains dark pink. In the muscularis externa, the two layers – inner (ic) and outer (ol), or circular and longitudinal – can be distinguished, although cell nuclei appear elongated in both cases because of the oblique plane of sectioning in this preparation. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 1.02 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_20X_67_69_collageB.jpg | Oblique section of the small intestine in a rat (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 956.67 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_vessels_16x_09_LETTERS.jpg | Villi in the small intestine in mice. The villus at the centre (asterisk) exhibits the typical finger-like form, with a thin epithelium (ep) lining the surface and staining dark pink, and a lamina propria (lp) in the core of the villus. This lamina propria contains numerous capillaries (c, bidirectional dashed segments) and dispersed cells, some of which are stained dark purple and are likely lymphocytes (ly). In the villus to the left, the simple – mono-layered – epithelium is readily recognised (mono-), with the cell nuclei stained dark purple (white arrows) and located in deep zones of the cells. In contrast, the cytoplasm in the apical portions of the cells is stained dark pink, and the border – the brush border (black arrowhead) – is seen as a dark line at this magnification. Goblet cells (Go) are dispersed between the other epithelial cells, and their round mass of mucous secretory granules stains greyish (Go, and white arrowheads). Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 791.65 kB | JPEG | 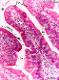 View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_vessels_16x_09.jpg | Villi in the small intestine in mice. No labelling. | 738.62 kB | JPEG | 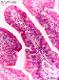 View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_brush_40x_16_LETTER.jpg | Tip of a villus in the small intestine in mice. The epithelium is tall and spans from the lamina propria (lp, dashed line) to the surface. Nuclei (N) are stained dark purple and lie in deep portions of the cells, forming a single row of nuclei: a simple or mono-layered epithelium. Cells are tall and their cytoplasm is dark pink. They are absorptive cells, and electron microscopy reveals that the apical surface presents a dense band of microvilli, which are not visible as such in light microscopy, but appear as a dark rim called the "brush border" (arrows). Intercalated between the absorptive cells, there are mucus-secreting cells – the goblet cells – with a round area accumulating mucous secretory granules that appear as round grey masses (asterisks). When the image is enlarged, individual mucous secretory granules are faintly perceptible there. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 538.01 kB | JPEG | 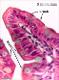 View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_brush_40x_16.jpg | Tip of a villus in the small intestine in mice. No labelling. | 486.49 kB | JPEG | 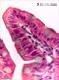 View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_vessels_6_3x_06_LETTERS.jpg | Inner portions of the small intestine wall in mice. The deeper end of various crypts (asterisks) is visible, consisting of absorptive cells that stain purple, but a few secretory cells with bright pink secretory granules – the Paneth cells (Pa) – can be seen at the end of each crypt. Small portions of lamina propria (lp) can be distinguished between crypts. The inner border of the mucosa consists of a thin layer of smooth muscle cells: the muscularis mucosæ (mm). The submucosa (sub) is thin but protrudes upwards into the mucosa because of the presence of large blood vessels: an artery (ar) and a vein or two (ve). In this transverse histological section, cell nuclei in the inner – or circular –muscular layer (ic) are elongated while those in the outer – or longitudinal – muscular layer (ol) appear round due to transverse sectioning. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 738.96 kB | JPEG | 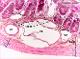 View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_vessels_6_3x_06.jpg | Inner portions of the small intestine wall in mice. No labelling. | 667.34 kB | JPEG | 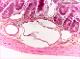 View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_40x_12_14_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Deep layers in the small intestine in mice (collage of micrographs allowing detailed zoom). The inner portion of the mucosa is observed containing the bottom of some crypts (asterisks). There, cells are stained purple except for some with mucous secretory granules – stained light grey – and the Paneth cells (Pa), located at the bottom of the crypts and containing bright pink secretory granules. Between the crypts, dispersed cells of the lamina propria (lp) are visible. The deepest portion of the mucosa consists of the muscularis mucosæ layer (mm), composed of smooth muscle cells stained bright pink. Between the muscularis mucosæ and the muscularis externa, a narrow submucosa (sub) is located containing blood vessels (v) and neurones (Neu) of the submucosal – or Meissner's – plexus. In the muscularis externa, the nuclei of the smooth muscle cells in the inner/circular layer (ic) are elongated in this transverse section of the intestine, while those in the outer/longitudinal layer (ol) appear rounded in section, although they are also elongated. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 811.21 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_40x_12_14_collage.jpg | Deep layers in the small intestine in mice (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 736.13 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_40x_13_collageB_LETTERS.jpg | Deep layers in the small intestine in mice (detail from a previous figure). The end of a crypt is observed on the right (asterisk) surrounded by the matrix and cells of the lamina propria (lp). In the muscularis mucosae (mm), some smooth muscle cells are sectioned longitudinally and appear thin, while a small bundle is cut transversally and shows dark purple nuclei, which are round in section, surrounded by bright pink cytoplasm. In the submucosa (sub), in addition to thick collagen fibres (empty arrowheads), a large neurone of the submucosal or Meissner's plexus is observed with a pale, large oval nucleus and a dark nucleolus. In the muscularis externa, nuclei in the internal/circular layer are cut along their length, and in the outer/longitudinal layer are cut transversally and appear round, although they are actually elongated. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. v, blood vessels. | 512.15 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_intestine_Heosin_40x_13_collageB.jpg | Deep layers in the small intestine in mice (detail from a previous figure). No labelling. | 462.26 kB | JPEG | 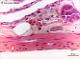 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_100X_73_Paneth_LETTERS.jpg | Paneth cell in deep portions of a crypt in the rat intestine. The deep end of this crypt is surrounded by the lightly-stained lamina propria (lp). Paneth cells have a dark purple nucleus (NˬP) in the basal part of the cell, and bright pink secretory granules (gr) in the apical part. Enterocytes – the absorptive cells – also have dark purple nuclei (Nˬe) in the basal part but – in contrast to Paneth cells – lack secretory granules in the apical region. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. L, lumen of the crypt; v, blood vessels. | 480.32 kB | JPEG | 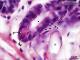 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_100X_73_Paneth.jpg | Paneth cell in deep portions of a crypt in the rat intestine. No labelling. | 453.77 kB | JPEG | 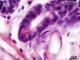 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_50X_75_submuc_glands_LETTERS.jpg | Islet of Brunner's glands in the submucosa of the duodenum in a rat. These glands are generally described as tubular. This islet is located just underneath the muscularis mucosæ (mm, in the upper right corner). The centre of each secretory mass in the islet presents a lumen (L) which can be wider (compatible with a tubular gland) or narrower. Cell nuclei (N) are located in the periphery (basal part of the cells) and are stained dark purple, with a darker nucleolus noticeable in some of them. The apical part of the cells, towards the lumen, appears to contain large secretory granules with mucus, which are lightly stained. The islet is surrounded by delicate collagen fibres (empty arrowheads) and some connective tissue cells: fibroblasts (fi) and a likely plasma cell (pl). Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 625.83 kB | JPEG | 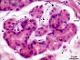 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_50X_75_submuc_glands.jpg | Islet of Brunner's glands in the submucosa of the duodenum in a rat. No labelling. | 593.91 kB | JPEG | 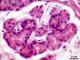 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_50X_70_Meissner_LETTERS.jpg | Neurone in the submucosal – Meissner's – plexus in the small intestine in a rat. In this deep zone of the intestinal wall, a small portion of the lamina propria (lp) and the muscularis mucosæ (mm) are seen in the upper right corner. Adjacent to them, there is a thin submucosa layer (sub) containing thick collagen fibres (empty arrowheads) with small cells interspersed. Additionally, large neurones of the Meissner or submucosal plexus (M/s) can be observed. Neuronal nuclei are large and palely stained, with a prominent nucleolus (better seen in the cell on the right). Underneath the submucosa, two muscular layers are present: inner/circular (ic) and outer/longitudinal (ol). In this longitudinal section of the intestine, smooth muscle cell nuclei in the inner layer (Nˬi) appear round, and in the outer layer (Nˬo) appear elongated. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. ser, serosa layer; ve, vein. | 624.1 kB | JPEG | 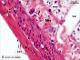 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_50X_70_Meissner.jpg | Neurone in the submucosal – Meissner's – plexus in the small intestine in a rat. No labelling. | 554.48 kB | JPEG | 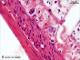 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_50X_78_ganglion_LETTERS.jpg | Neurones in the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus in the small intestine in a rat. To the right, deep portions of the mucosa are shown including epithelial cells (ep) in a crypt and the muscularis mucosæ layer (mm). The submucosa (sub) contains thick collagen fibres (empty arrowheads) stained dark pink and some scattered cells. In the muscularis externa, between the inner or circular layer (ic) and the outer or longitudinal layer (ol), a ganglion of Auerbach's – myenteric – plexus (A/m) is observed. It contains large cells, and two of them can clearly be identified as neurones by their pale nucleus and prominent nucleolus. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 636.15 kB | JPEG | 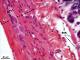 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_50X_78_ganglion.jpg | Neurones in the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus in the small intestine in a rat. No labelling. | 580.87 kB | JPEG | 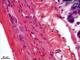 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_100X_78_ganglion_LETTERS.jpg | Detail of a nerve ganglion in the small intestine in a rat. The two layers of the muscularis externa can be distinguished by the profiles of the sectioned nuclei of the smooth muscle cells. Nuclear sections in the inner/circular layer (ic) appear round (Nˬi) while those in the outer/longitudinal layer (ol) appear elongated (Nˬo), as they are sectioned along their longitudinal axis. Between these layers, a nerve ganglion of Auerbach's – myenteric – plexus (A/m) is located. Neurones are large (neu), with a lightly stained nucleus and a dark purple nucleolus. Paraffin section, hæmatoxylin-eosin stain. | 607.51 kB | JPEG | 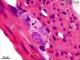 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_HEosin_100X_78_ganglion.jpg | Detail of a nerve ganglion in the small intestine in a rat. No labelling. | 575.3 kB | JPEG | 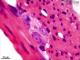 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_4x_HEosin47_vGieson01_LETTERS.jpg | Rat duodenum and adjoining pancreas: comparison of hæmatoxylin-eosin stain (left) and van Gieson trichrome (right). Intestinal villi (black arrowheads) appear as finger-shaped projections. They are lined with a simple – single-layered – epithelium, which is darkly stained and extends into the mucosa, forming crypts. The core of the villi is occupied by the palely stained lamina propria (lp), which also extends between the crypts. The deeper border of the mucosa consists of a thin layer of smooth muscle cells termed the muscularis mucosæ (mm), which stains pink with eosin (left) and light brown with van Gieson trichrome (right). Beneath the muscularis mucosæ lies the submucosa (sub), a connective tissue layer rich in collagen fibres that stain pink with eosin (left) and bright fuchsia with van Gieson's acid fuchsin (right). The underlying muscularis externa (me) is a compact layer of muscle cells that stain dark pink with hæmatoxylin-eosin (left), and pale brown with van Gieson trichrome, which allows a clear distinction between the muscular layers and the submucosa. The duodenal wall is linked to the pancreatic acini by the mesenterium and its blood vessels: arteries (ar) and veins (ve). Paraffin section. | 1.3 MB | JPEG | 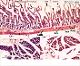 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_4x_HEosin47_vGieson01.jpg | Duodenum and the adjoining pancreas in a rat compared in hæmatoxylin-eosin and van Gieson stains. No labelling. | 1.21 MB | JPEG | 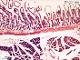 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_4x_01_02_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Longitudinal section of the duodenum and the adjoining pancreas in a rat (collage of micrographs allowing moderate zoom). Mucosa forms finger-like projections termed villi (black arrowheads). They are lined with a darkly stained simple epithelium that also invaginates into the mucosa, forming crypts. In the core of the villi and surrounding the crypts lies a loose connective tissue that stains palely: the lamina propria (lp). A thin muscularis mucosæ (mm) defines the deepest border of the intestinal mucosa. Beneath it, the submucosa (sub) stands out for its numerous collagen fibres, which stain bright fuchsia, and its blood vessels (v). Beneath the submucosa lies the muscularis externa (me), which is divided into two sublayers – inner and outer – although not distinguishable at this magnification. On the right, branches of the pancreaticoduodenal arteries (ar) and veins (ve) can be seen crossing the muscularis externa to branch into the submucosa. Next to this portion of the duodenum, pancreatic acini are grouped in numerous lobules separated by loose connective tissue that appears virtually unstained. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 1.06 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_4x_01_02_collage.jpg | Longitudinal section of the duodenum and the adjoining pancreas in a rat (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 1.01 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_20X_80_83_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Layers in the duodenal wall in a rat (collage of micrographs allowing detailed zoom). Villi are lined with a simple columnar epithelium (ep): a single-layered epithelium of tall cells (white bidirectional arrows) with a light brown cytoplasm. In the villus at the centre (black star), it is evident that the dark oval cell nuclei (N) are aligned in a single row at the base of the cells. Interspersed between the absorptive cells – stained brown – lie the goblet cells, which contain a round mass of mucous secretory granules that stain light violet or lilac (Go, white arrowheads). The core of the villi consists of a loose connective tissue – the lamina propria (lp) – with a light matrix, blood vessels (v), and scattered cells. In deep portions of the mucosa, crypts are observed: they are folds of the surface epithelium, although here they were cut obliquely and the continuity with the surface is not observed. The deepest part of the mucosa is the muscularis mucosæ (mm): a thin layer of smooth muscle cells with dark elongated nuclei and light brown cytoplasm. The submucosa (sub) lies just beneath the muscularis mucosae. It contains thick collagen fibres (empty arrowheads), which stain dark fuchsia with van Gieson trichrome. In this micrograph, the submucosa contains islets of Brunner's glands (g), which cover most of the submucosa and, in some regions, interrupt the muscularis mucosæ and extend into the lamina propria. Underlying the submucosa, the two layers of the muscularis externa are observed: the inner or circular layer (ic) of smooth muscle cells and the outer or longitudinal layer (ol). A nerve ganglion of the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus (A/m) appears to be located between these two layers (to the right), but is difficult to identify at this magnification. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 1.72 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_20X_80_83_collage_tip.jpg | Layers in the duodenal wall in a rat (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 1.6 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_50x_19_23_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Detail of the layers in the small intestine in a rat (collage of micrographs allowing detailed zoom). The base of a villus is seen at the top: it is lined with a simple columnar epithelium (ep) containing absorptive cells with a dark nucleus and pale brown cytoplasm, and goblet cells with a round accumulation of mucus located apically and stained lilac (Go). The surface epithelium invaginates into the mucosa, forming crypts, in which proliferative cells undergo mitosis (black arrowheads) to constantly renew the epithelium of the villi. Inside the villi and between the crypts, a palely stained lamina propria (lp) is present: a lightly stained matrix accommodates darkly stained cells and numerous blood vessels (v and bidirectional dashed segment). The inner border of the mucosa consists of a thin layer of smooth muscle cells: the muscularis mucosae (mm). Beneath this lies the submucosa (sub) containing many blood vessels – arteries (ar), veins, and capillaries (c) –, scattered cells, and a dense matrix of collagen fibres vividly stained with acid fuchsin. Underneath, a thick layer of smooth muscle cells is observed, with a pale brown cytoplasm and dark nucleus. According to the cell orientation, this layer is divided into two: an inner or circular layer (ic) and an outer or longitudinal layer (ol). In this longitudinal section of the intestine, the elongated cell nuclei appear as round sections in the inner/circular layer, while they can be seen at full length in the outer/longitudinal layer. Between these two muscular layers, ganglia of the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus can be observed (Gn). A thin serosa (ser) forms the external envelope of the tube. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 1.39 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_50x_19_23_collage.jpg | Detail of the layers in the small intestine in a rat (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 1.28 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_100x_42_LETTERS.jpg | Surface of a villus in the small intestine of a rat. Villi are lined with a simple columnar epithelium: tall cells with an oval nucleus at the base and a brown cytoplasm that shows a more contrasted apical band, forming the brush border. The lamina propria contains scattered cells, a matrix with delicate collagen fibres stained pink (empty arrowhead), and a network of blood and lymph vessels, with a network of capillaries (c) just underlying the epithelium. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 545.58 kB | JPEG | 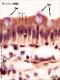 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_100x_42.jpg | Surface of a villus in the small intestine of a rat. No labelling. | 499.89 kB | JPEG | 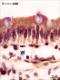 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_50X_89_crypt_LETTERS.jpg | Crypts in deep portions of the intestinal mucosa in a rat. The epithelium forms pits into the mucosa – the crypts – with the intestinal lumen at the centre (L) and the single-layered epithelium around it, with dark oval cell nuclei (N). Mucus accumulations in goblet cells are stained light violet (Go). Proliferative cells in various crypts are undergoing mitosis and display condensed chromosomes (empty arrowheads). The lamina propria (lp) fills the space between the crypts and contains scattered cells, a matrix with delicate collagen fibres stained light pink (black arrowheads), and blood vessels. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. ve, vein. | 697.95 kB | JPEG | 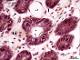 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_50X_89_crypt.jpg | Crypts in deep portions of the intestinal mucosa in a rat. No labelling. | 671.22 kB | JPEG | 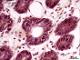 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_100X_95_crypt_LETTERS.jpg | Crypts in the intestinal mucosa in a rat. The epithelium in the crypts consists of a single layer of tall – columnar – cells. The nucleus (N) is located at the base (periphery of the crypt) and contains dark chromatin granules and a nucleolus (nu). A cell in mitosis (empty arrowhead) – probably in anaphase – is present and exhibits condensed chromosomes. Round accumulations of mucous secretory granules in goblet cells are observed (Go, dashed circles; lilac tint), and the individual granules are faintly delineated. In the lamina propria enveloping the crypts, delicate collagen fibres can be seen stained light pink (black arrowheads). Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 550.73 kB | JPEG | 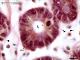 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_100X_95_crypt.jpg | Crypts in the intestinal mucosa in a rat. No labelling. | 525.03 kB | JPEG | 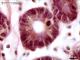 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_100X_96_crypt_LETTERS.jpg | Crypts in the intestinal mucosa in a rat: mitotic cells. A narrow lumen is seen in the centre of the crypt, surrounded by a simple columnar epithelium with cell nuclei (N) located in basal portions of the cells (in the periphery of the crypt). In many nuclei, dark and small chromatin clumps are observed, including a nucleolus. Cells undergoing mitosis show condensed chromosomes (empty arrowheads). Crypts are enveloped by the lamina propria, which contains thin collagen fibres stained light pink (black arrowheads), scattered cells, capillaries (bidirectional dashed segment), and larger blood vessels (v). Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 536.93 kB | JPEG | 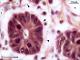 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_100X_96_crypt.jpg | Crypts in the intestinal mucosa in a rat: mitotic cells. No labelling. | 519.76 kB | JPEG | 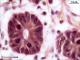 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_20X_88_crypts_MM_subm_LETTERS.jpg | Mucosa and submucosa interface in the rat duodenum. The lamina propria (lp) is lightly stained and contains scattered cells and numerous blood vessels (v). Deep portions of the crypts (c) are sectioned obliquely, and the connection with the surface cannot be observed. In these crypts, the absorptive cells are stained brown, and the mucous accumulations in the goblet cells (Go) are stained lilac. The deep border of the mucosa consists of a thin layer of smooth muscle cells – the muscularis mucosæ (mm) – with dark elongated nuclei. Beneath this lies the submucosa (sub), which contains numerous islets of Brunner's glands (g) in this part of the duodenum. The islets are round, with a relatively large lumen (L) and brown cells that stain lighter than those in the crypts. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 1.03 MB | JPEG | 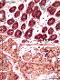 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_20X_88_crypts_MM_subm.jpg | Mucosa and submucosa interface in the rat duodenum. No labelling. | 972.54 kB | JPEG | 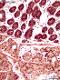 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_50X_98_muscularis_mucosae_LETTERS.jpg | Muscularis mucosæ (mm) in the rat duodenum. The smooth muscle cells were cut longitudinally, and the nuclei (Nˬm) appear elongated and moderately stained. In the overlying lamina propria (lp), thin collagen fibres are stained pink (empty arrowheads). Three crypts (c) appear transversely cut: epithelial cells are stained dark brown, except for the mucous mass of goblet cells (Go), which stains lilac. A small lumen (Lˬc) is seen in the centre of each crypt. Beneath the muscularis mucosa lies the submucosa, which contains islets of Brunner's glands (g) in this section. Their cells have a moderately dark nucleus (Nˬg) and a light brown cytoplasm, with some unevenness suggestive of secretory granules. Collagen fibres stained pink surround the islets (empty arrowheads). Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. L, lumen of Brunner's glands; N, nucleus of an epithelial cell; v, blood vessel. | 738.38 kB | JPEG | 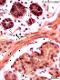 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_50X_98_muscularis_mucosae.jpg | Muscularis mucosæ in the rat duodenum. No labelling. | 673.5 kB | JPEG | 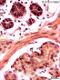 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_50X_92_glands_LETTERS.jpg | Brunner's glands in the duodenal submucosa in rats. The submucosa (sub) is rich in collagen fibres (empty arrowheads), which stain vividly with acid fuchsin. This connective tissue surrounds the islets of Brunner's glands. These are described as tubular glands, which appear as rings in this section. In the centre lies the lumen (L), unstained, which is surrounded by a single-layered epithelium. These cells have a dark nucleus (N) with few chromatin clumps and a distinct nucleolus. The cytoplasm stains light brown with darker inner lines that appear to delineate secretory granules. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. | 711.62 kB | JPEG | 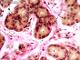 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_vGieson_50X_92_glands.jpg | Brunner's glands in the duodenal submucosa in rats. No labelling. | 678.11 kB | JPEG | 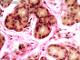 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_neurones_50x_26_27_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Deep layers in the small intestine in rats (collage of micrographs allowing moderate zoom). The submucosa (sub) appears as a connective tissue rich in thick collagen fibres, which stain intensely with acid fuchsin (empty arrowheads). A few cells are scattered throughout this matrix. The underlying muscular layer stains light brown and can be easily distinguished from the submucosa. In the inner muscular layer (ic), muscle fibres are oriented circularly around the lumen. As a result, the elongated nuclei of smooth muscle cells are sectioned transversely and appear as round profiles in this longitudinal view of the intestine. In contrast, nuclei in the outer – longitudinal – muscular layer (ol) can be recognised as elongated. Between these two muscular layers, ganglia of the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus (Gn) are observed. Neurones (neu) and satellite cells (sat) can be identified at this magnification. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. v, blood vessels. | 712.79 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_neurones_50x_26_27_collage.jpg | Deep layers in the small intestine in rats (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 667.16 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_neurones_100x_34_LETTERS.jpg | Ganglion of the myenteric plexus in the small intestine in a rat. The ganglion is located between the inner/circular (ic) and outer/longitudinal (ol) muscular layers. It is surrounded by a thin envelope of fibroblasts (fi) and collagen fibres (black arrowheads), which stain pink. Within the ganglion, large neurones (neu) can be seen with a large nucleus and a prominent nucleolus (empty arrowhead). Smaller cells with darker nuclei are likely to be enteric glial cells (egc). Large round satellite cells (sat) are seen at the periphery. Paraffin section, van Gieson trichrome. c, capillary; Nˬc, nuclei of muscle cells in the inner muscular layer; Nˬl, nuclei of muscle cells in the outer muscular layer. | 635.74 kB | JPEG | 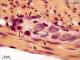 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum_vanGieson_neurones_100x_34.jpg | Ganglion of the myenteric plexus in the small intestine in a rat. No labelling. | 575.27 kB | JPEG | 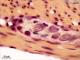 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_2x_06_07_collageC_LETTERS.jpg | General view of the duodenum and pancreas in a rat in a semi-thin section. The duodenum presents a mucosa that forms finger-like protrusions – the villi (empty arrowheads) –. These are lined by a single-layered epithelium and contain a loose connective tissue – the lamina propria (asterisks) –. The palely stained narrow layer beneath the mucosa is the submucosa, and the greyish external layer is the muscularis externa (me). In the mesenterium attached to the duodenum, masses of adipose tissue appear black due to osmium tetraoxide. Pancreatic lobules can also be observed. In rats, these are diffusely distributed along the duodenum and do not form a compact organ. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 672.62 kB | JPEG | 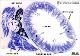 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_2x_06_07_collageC.jpg | General view of the duodenum and pancreas in a rat in a semi-thin section. No labelling. | 620.83 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_4x_03_04_collageB_LETTERS.jpg | Duodenal wall and adjoining pancreas in a rat. Villi protrude from the surface (empty arrowheads). They are lined by a simple epithelium (ep) and enclose the lamina propria (asterisks). The epithelium also extends into the mucosa, forming crypts (cry). A thin muscularis mucosae (mm) is barely noticeable at this magnification and forms the deepest limit of the mucosa. Adjacent to it lies the submucosa (sub), which is narrow and palely stained, and then the muscularis externa (me). In the loose connective tissue of the mesenterium, adipose tissue (fat) and blood vessels (v) are observed. In the pancreas, lobules containing secretory acini and some islets are present. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 866.88 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_4x_03_04_collageB.jpg | Duodenal wall and adjoining pancreas in a rat. No labelling. | 822.64 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_20x_11_13_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Organisation of the duodenal wall in a rat (collage of micrographs allowing moderate zoom). Three villi are observed. They are covered by a single-layered epithelium (ep) composed of tall cells (white bidirectional arrows, ↔), i.e. a simple columnar epithelium. Goblet cells in the epithelium contain a round mass of mucous granules (Go) stained dark blue. The epithelium also forms deep pits in the wall termed crypts (c). Within the villi, a lamina propria (lp) is present with scattered cells and numerous vessels (v). It also occupies the space between the crypts. The deepest border of the mucosa is a thin layer of smooth muscle cells: the muscularis mucosæ (mm). Beneath this lies the submucosa (sub) which is also rich in blood vessels. The muscularis externa is more darkly stained and can be divided into an internal – circular – layer (ic) and an outer – longitudinal – layer (ol). Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 1.07 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_20x_11_13_collage.jpg | Organisation of the duodenal wall in a rat (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 1.01 MB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_duodenum_semithin_2um_40x_19_22_collage_LETTERS.jpg | Deep layers in the duodenal wall (collage of micrographs allowing moderate zoom). Some crypts are observed in deep regions of the mucosa. Epithelial cell nuclei are lightly stained (N) and the mucous accumulations in goblet cells are stained dark blue (Go). The bottom of the crypt on the left was cut tangentially at the level of the cell nuclei, resulting in a compact cluster of nuclei. Between the crypts, a lightly stained lamina propria (lp) is observed with scattered cells and vessels (v). The muscularis mucosæ (mm) consists of 2-3 layers of smooth muscle cells cut transversally in this sample, appearing as round cell profiles. The submucosa (sub) is also a connective tissue layer but denser (with thicker collagen fibres) than the lamina propria. In the muscularis externa, smooth muscle fibres in the inner/circular layer (ic) are seen elongated, since this semi-thin section is a transversal section of the duodenum, while the cells in the outer/longitudinal layer (ol) appear as round profiles due to transverse sectioning. Between the two layers in the muscularis externa, a nerve ganglion of the myenteric – Auerbach's –plexus is observed (Gn). Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 923.96 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_duodenum_semithin_2um_40x_19_22_collage.jpg | Deep layers in the duodenal wall (collage of micrographs). No labelling. | 870.08 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_duodenum_semithin_2um_40x_13_LETTERS.jpg | Tip of a villus in the rat duodenum. The epithelium consists of a single layer of tall cells (ep, bidirectional arrows ↔). The cell nucleus is lightly stained and located at the base of the cell, while the cytoplasm is darker. At the apical surface of the epithelial cells, the brush border is clearly observed: it corresponds to the thousands of microvilli seen in electron microscopy. Dark accumulations of mucous granules are observed in the apical part of goblet cells (Go, white arrowheads). Beneath the epithelium, a light lamina propria (lp) is observed. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 430.94 kB | JPEG | 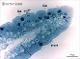 View/Open |
| P_duodenum_semithin_2um_40x_13.jpg | Tip of a villus in the rat duodenum. No labelling. | 393.09 kB | JPEG | 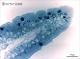 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_40_epithelium_LETTERS.jpg | Villi in the rat duodenum. The epithelium consists of tall cells (ep, bidirectional dashed arrows) with a lightly stained nucleus (N) at the base and a darker cytoplasm. The apical surface displays the brush border, which corresponds to the microvilli seen in electron microscopy. The lamina propria (lp) lies in the core of the villus and contains numerous capillaries (c) just beneath the epithelium. On the left, three tangential sections of villi (1, 2, and 3) are observed, all delineated by a brush border. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. brush, brush border; Go, mucous accumulation in the apical part of goblet cells. | 798.31 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_40_epithelium.jpg | Villi in the rat duodenum. No labelling. | 754.01 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_22_epithelium_LETTERS.jpg | Absorptive epithelium in two neighbouring villi (1 and 2) in the rat duodenum. The epithelium (ep) consists of tall cells (white bidirectional dashed arrows) with a dark cytoplasm and a brush border at the surface (black arrows). In the apical part of goblet cells, round accumulations of mucus are stained dark blue (Go). Nuclei (N) are unstained and not perfectly aligned due to the tangential section of these villi. Inside villus 1, the lamina propria with scattered cells is observed. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 890.41 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_22_epithelium.jpg | Absorptive epithelium in two neighbouring villi in the rat duodenum. No labelling. | 851.4 kB | JPEG | 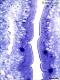 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_100X_41_epithelium_LETTERS.jpg | The villus surface in the rat duodenum at high magnification. Epithelial cells are tall (white bidirectional dashed arrows). They have oval nuclei (N) aligned in a single row, characteristic of a simple columnar epithelium. The apical surface is arranged in a brush border – grouping of microvilli – with neat boundaries (black arrows). In goblet cells, the secretory granules accumulate apically, forming a round mass stained dark blue (Go). Just beneath the epithelium, the lamina propria (lp) contains a profuse network of capillaries with an empty lumen (c) and the nuclei of endothelial cells in the wall (e). Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 760.6 kB | JPEG | 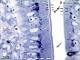 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_100X_41_epithelium.jpg | The villus surface in the rat duodenum at high magnification. No labelling. | 713.24 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_24_crypt_LETTERS.jpg | Deep layers in the duodenal mucosa in a rat. The epithelium in the villus invaginates into the mucosa, forming a crypt. Cells are tall (white bidirectional arrows) and cell nuclei (N) are oval and arranged in a single row. In goblet cells, mucous secretory granules are grouped in a round mass stained dark blue (Go). The brush border can be observed in the cells located higher in the villus, but the lumen in the crypt was cut tangentially, preventing visualisation of the brush border. The lamina propria (lp) surrounds the crypts. It contains few cells, a light matrix, capillaries (c) and larger vessels (v). The deep border of the mucosa is marked by two rows of smooth muscle cells cut transversally (round profiles) which constitute the muscularis mucosæ (mm). Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. | 836.35 kB | JPEG | 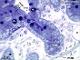 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_24_crypt.jpg | Deep layers in the duodenal mucosa in a rat. No labelling. | 777.42 kB | JPEG | 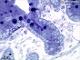 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_47_mmucosae_LETTERS.jpg | Deep layers in the duodenal wall in a rat. The muscularis mucosæ (mm, arrows) is sharply delimited. In this layer, smooth muscle cells were sectioned transversally and are arranged in three or four layers of round profiles. Overlying the muscularis mucosa, a pale lamina propria (lp) and the bottom of three crypts (1, 2, 3) are observed. Beneath the muscularis mucosæ lies the submucosa (sub), a layer of connective tissue with thick collagen fibres (empty arrowheads) and various vessels: arterioles (ar) and veins (ve). The previously mentioned lamina propria is also a connective tissue with blood vessels (v) but it lacks the thick collagen fibres characteristic of the submucosa. Beneath the submucosa, the inner – circular – layer of smooth muscle (ic) is observed with cells cut longitudinally. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. Go, mucous granules in goblet cells; N, nucleus in an epithelial cell in a crypt. | 883 kB | JPEG | 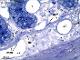 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_47_mmucosae.jpg | Deep layers in the duodenal wall in a rat. No labelling. | 810.88 kB | JPEG | 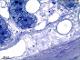 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_16_Meissner_LETTERS.jpg | Meissner ganglion in the duodenal submucosa in a rat. The submucosa (sub) appears as a thin layer with numerous blood vessels (v). Here, a nerve ganglion of the submucosal – Meissner's – plexus (M/s) is observed. It contains three large neurones, the one on the left displaying a large nucleus and a distinct nucleolus, typical of neurones. The submucosa is limited internally by the muscularis mucosæ (mm) and externally by the muscularis externa that comprises an inner – circular – layer (ic) and an outer – longitudinal – layer (ol). Between them, elements of the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus (A/m) can be observed. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. c, capillary; Go, mucous granules in goblet cells; N, nucleus in an epithelial cell in a crypt. | 881.14 kB | JPEG | 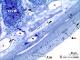 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_16_Meissner.jpg | Meissner ganglion in the duodenal submucosa in a rat. No labelling. | 814.57 kB | JPEG | 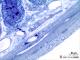 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_46_ganglia_LETTERS.jpg | Submucosal – Meissner – plexus in the duodenal wall in a rat. The submucosa (sub) appears as a thin layer with blood vessels (v) and thick collagen fibres stained light blue. In this layer, ganglia of the submucosal – Meissner's – plexus (M/s) are observed: neurones show a large pale nucleus and dark cytoplasm. The submucosa (sub) is limited internally by the muscularis mucosæ (mm) and externally by the muscularis externa, which comprises an inner – circular – layer (ic) and an outer – longitudinal – layer (ol). Between these, elements of the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus (A/m) can be observed. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. c, capillary. | 911.38 kB | JPEG | 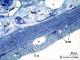 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_46_ganglia.jpg | Submucosal – Meissner – plexus in the duodenal wall in a rat. No labelling. | 861.31 kB | JPEG | 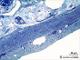 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_100X_44_ganglia_LETTERS.jpg | Submucosal neurone in the duodenal wall in a rat. In the submucosa (sub), a neurone of the Meissner's plexus (M/s) is observed. It has a large nucleus with a dark nucleolus and dark blue cytoplasm. In the muscularis externa, between the inner/circular layer (ic) and the outer/longitudinal layer (ol), elements of the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus (A/m) can be observed. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. c, capillary. | 819.39 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_100X_44_ganglia.jpg | Submucosal neurone in the duodenal wall in a rat. No labelling. | 789.85 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_32_ganglia_LETTERS.jpg | Deep layers in the duodenum including a myenteric ganglion. The lower ends of three crypts (1, 2 and 3) are closely apposed to the muscularis mucosæ layer (mm, white arrowheads). A palely stained lamina propria (lp) envelopes the crypts. The submucosa (sub) is narrow and overlies the muscularis externa, which can be divided into an inner/circular layer (ic) and an outer/longitudinal layer (ol). Between these two, a myenteric – Auerbach's – ganglion (A/m) is located, although individual neurones are not readily distinguishable. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. c, capillary; v, blood vessel. | 983.87 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_32_ganglia.jpg | Deep layers in the duodenum including a myenteric ganglion. No labelling. | 931.86 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_duodenum_semithin_2um_40x_18_LETTERS.jpg | Nerve ganglia in the duodenal wall in a rat. In the submucosa (sub) an isolated neurone of Meissner's plexus (neu) is observed containing a pale nucleus. In the muscularis externa, between the inner/circular layer (ic) and the outer/longitudinal layer (ol), a ganglion of the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus (Gn) contains three large neurones with pale nuclei. In two of them, the nucleolus is faintly visible. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. c, capillary; mm, muscularis mucosæ; ve, venule. | 523.22 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_duodenum_semithin_2um_40x_18.jpg | Nerve ganglia in the duodenal wall in a rat. No labelling. | 478.17 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_34_ganglia_LETTERS.jpg | Myenteric ganglion in the duodenal wall in a rat. The muscularis externa is divided into two layers; an inner – circular – layer (ic) and an outer – longitudinal – layer (ol). The smooth muscle cells in the outer layer are cut transversally and appear as round or oval profiles (inset). Between these muscle layers, three neurones of a myenteric ganglion (A/m) are observed, each with a light nucleus and dark blue cytoplasm. Inset: Detail of the outer – longitudinal – layer of the muscularis externa. Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. c, capillary; mm, muscularis mucosae; sub, submucosa; ve, venule. | 854.1 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_50X_34_ganglia.jpg | Myenteric ganglion in the duodenal wall in a rat. No labelling. | 802.22 kB | JPEG | 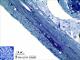 View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_100X_45_ganglia_LETTERS.jpg | Neurones in the myenteric plexus in the rat duodenum. In the muscularis externa, between the inner – circular – layer (ic) and the outer – longitudinal – layer (ol), three neurones of the myenteric – Auerbach's – plexus (A/m) are seen (arrowheads). In two of them, the nucleolus is observed within a pale nucleus (empty arrowheads). Smooth muscle cells in the outer – longitudinal – layer (ol) were sectioned transversally, appearing as rounded or polygonal profiles (sm). Osmium tetraoxide postfixation, epoxy section 2 µm thick, toluidine blue stain. c, capillary; sub, submucosa. | 768.16 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
| P_O_duodenum2_semithin2um_100X_45_ganglia.jpg | Neurones in the myenteric plexus in the rat duodenum. No labelling. | 736.7 kB | JPEG |  View/Open |
This item is licensed under a
Creative Commons License



